1.Research Methodoloy
Resarch Process
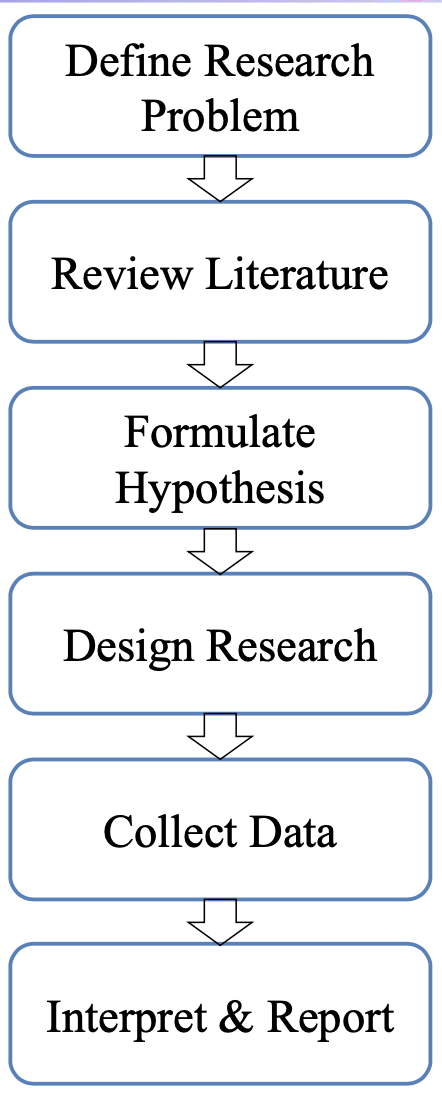
1.Literature Search
-
1.1 Web of Science • Previously known as Web of Knowledge. • It was originally produced by the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI). • Currently maintained by Clarivate Analytics (previously the Intellectual Property and Science business of Thomson Reuters). • Web of ScienceTM is the one of the most trusted publisher-independent global citation database. • WoS allows to track ideas across disciplines and time from almost 1.9 billion cited references from over 171 million records. • Citations are the formal, explicit linkages between papers that have particular points in common.
-
1.2 Microsoft Academic • Indexed an overview page that allow to easily explore top citing articles and references of the article. • Coverage : approx. 210 million articles • Abstracts • Related articles • References • Cited by • Links to full text • Export formats : APA, MLA, BibteX
-
1.3 BASE • Hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany • Coverage : approx. 136 million articles • Abstracts • No Related articles • No References • No Cited by • Links to full text • Export formats : RIS, BibTex
- 1.4 CORE
- 1.5 Science.gov
- 1.6 Semantic Scholar
- 1.7 Baidu Scholar
2.Why CITE?
- Ethics
- Intellectual honesty
- Attribution (tracking who said what when)
- Legal
- Attribution
- Copyright
- Research
- Attribution
- Evidence and support for authors’ claim Evidence of state-of-the-art
- Confidence in author
- Used as assessment of authors’ knowledge and understanding
- Reader convince
- Helps the reader to refer to useful related research
- Attribution
- The source of the idea
- E.g. “according to the work done by [x]”
- E.g. “as proved by x in [y]”
- Citation: specification of the source location, include all necessary details req uired to obtain the source (e.g. author names, title, where published, year, page n umber, URLs, location and date for conferences)
3.Objectives
- Milestone of the research
- Follows logically from the vision
- Task oriented break-down of projected work
- Task definition, one object to one task
- Task organization, task interrelations
- Task scheduling (Gannt Chart)
- Advantages
- Novelty, uniqueness, benefit (economic, time, efficiency)
- Measured against state-of-the-art and literature review
- Methodology
- Overall statement of advantages focused on process
- Follows logically from task definition
4.Problem Statement
- What is the research problem you aim to solve?
- What is the central research question? (ie What do you want to find out?)
- What will we know after completion of your work that we did not know before? (i.e. What is novel?)
- Why does it matter? (i.e. Why should someone care about this research?)
- Requires understanding of research area
- Literature review
- Web, news, and popular reading
- Advisers
- Graduate level courses
- Conferences (keynote, talks, and personal discussion)
- Requires statement of
- Research context (research field / sub-field)
- Significance
- Application to real world
- Benefit to human-kind, the world
5.Steps in defining a Problem
- Statement of the problem in a general way
- Understanding the nature of the problem
- Surveying the available literature
- Developing ideas through discussions
-
Rephrasing the research problem
- Methodology
- How do you (or plan to) conduct the research? Is it experimental or theoretical?
- How will you know that you have succeeded? (What is your plan to demonstrate the validity of your claims?)
- Explain briefly why your approach is appropriate in the context of your work. What alternatives would there be and why are you not using them?
- Related Work
- Briefly summarise the 4 most important publications for your research.
- How has this related work influenced your work?
- What is better (or different) in your work?
6.Professional Ethics
- Respect for intellectual property rights
- Academic honesty
- Give credit where credit is due
- Respect other’s contributions; evaluation of scholarship
- E.g.: Graduate students accomplishing their degree by rightfully claiming their contributions in print, Faculty rightfully claiming their contributions to support P&T.
- Promote a culture of mutual respect and contribution recognition: your contributions are like-wise to be recognized
- Correctly represent others’ works
- respectfully comment, review or critique others’ works
- Professional memberships
- ACM Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct
- IEEE Code of Ethics
7 Latex
• TeX is essentially a Markup Language (like HTML, XML and RTF) • TeX written by Donald Knuth in 70 ́s. • A revolution in typesetting . • Latex is an extension of TeX. • Macro packages to make TeX easier to use. • LaTeX is a document preparation system for high-quality typesetting. • LaTeX pronounced “lay-tech” or “lah-tech”. • not like latex gloves!
• Designed by academics and easily accommodates academic use. • Good for large documents • De facto standard for scientific publishing • Professional typesetting • Best output • It is the standard for scientific documents • Processing Mathematical (& other) symbols • Meaning-based structuring (rather than appearance) • Knowledgeable and helpful user group • Its FREE! • Platform independent
• MiKTeX • MiKTeX is a typesetting system for the Windows. • Download from www.miktex.org for free • It is generally recommended to install MiKTeX first, then WinEdt.
• WinEdt • WinEdt is a text editor. • WinEdt creates the source file (.tex and others). • Download from www.winedt.com for free for 30 days. • WinEdt costs $30.
• TexStudio • An integrated writing environment • For creating LaTeX documents. • Easy and comfortable • Syntax-highlighting, • Integrated viewer, • Reference checking, • Free.
-
File structure • Document Class • Predefined Formats (article, report,book,..).
-
Overleaf
• Overleafisacollaborativecloud-basedLaTeX editor. • Used for writing, editing and publishing scientific documents. • It partners with a wide range of scientific publishers to provide official journal LaTeX templates, and direct submission links.




Leave a comment