5.Image Restoration and Reconstruction
5.1 A Model of the Image Degradation/Restoration process
5.2 Noise Models
5.2.1 Spatial and Frequency properties of noise -CCD camera, light levels and sensor temperature are major factors affecting the amount of noise in the resulting image
5.2.2 Some Important Noise probability density functions -Gaussian noise , Rayleigh noise, Erlang noise , Exponential noise, Uniform noise, Impulse noise
5.2.3 Periodic Noise -Periodic noise in an image arises from electrical or electromechanical interference during image acquisition
5.2.4 Estimation of Noise parameters -The parameters of periodic noise are estimated by inspection of the Fourier spectrum of the image
5.3 Restoration in the presence of noise only-spatial filtering
5.3.1 Mean filters -Arithmetic mean filter, Geometric mean filter, Harmonic mean filter, Contraharmonic mean filter 5.3.2 Order statistic filters -Median filter, Max and min filters, Midpoint filter, Alpha-trimmed mean filter
5.3.3 Adaptive filters -Adaptive, local noise reduction filter, Adaptive median filter,
5.4 Periodic noise reduction by frequency domain filtering
5.4.1 Bandreject filters -Bandreject filtering is for noise removal in applications where the general location of the noise component
5.4.2 Bandpass filters -It performs the opposite operation of a bandreject filter
5.4.3 Notch filters -A notch filter rejects frequencies in predefined neighborhoods about a center frequency
5.4.4 Optimum notch filtering - It minimize local variances of the restored estimate
5.5 Linear, Position invariant degradations
5.6 Estimating the degradation function
5.6 Estimating the degradation function 5.6.1 Estimation by image observation
5.6.2 Estimation by Experimentation
5.6.3 Estimation by modeling
5.7 Inverse filtering
5.8 Minimum mean square error filtering
5.9 Constrained least squares filtering
5.10 Geometric mean filter
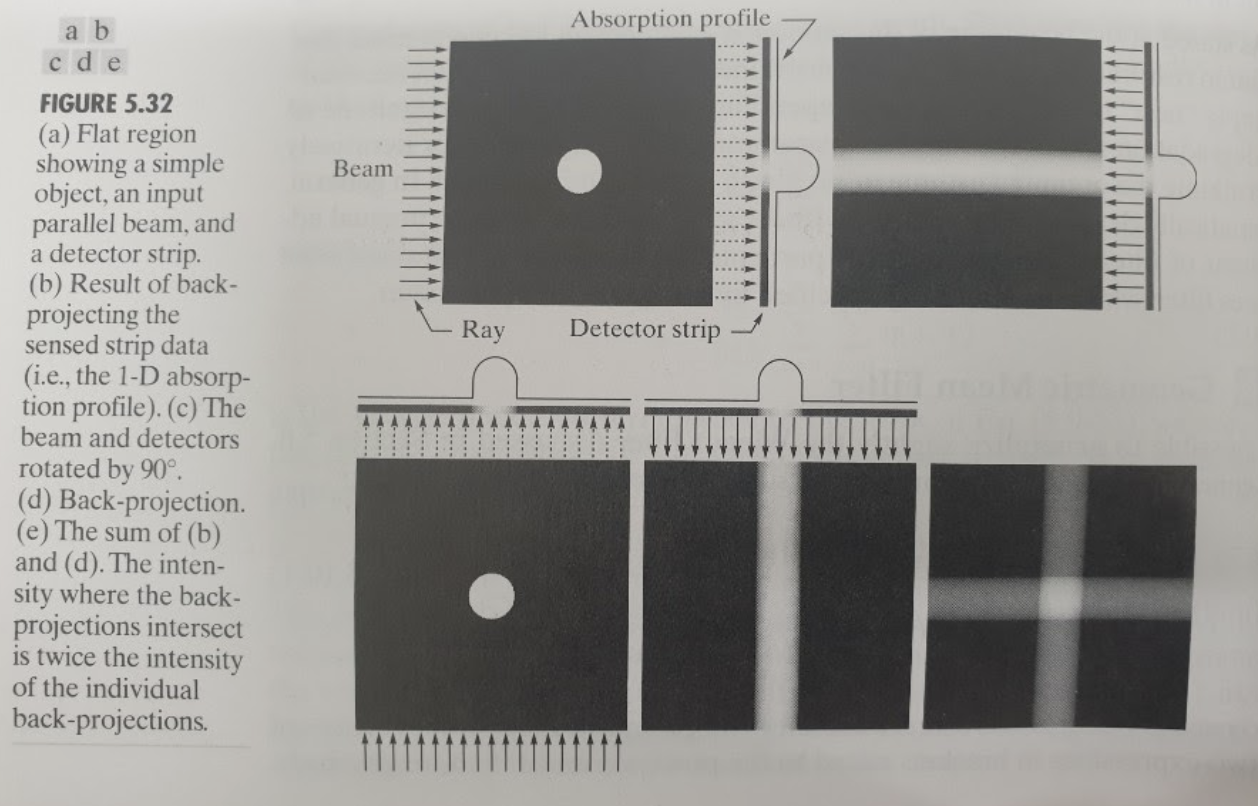
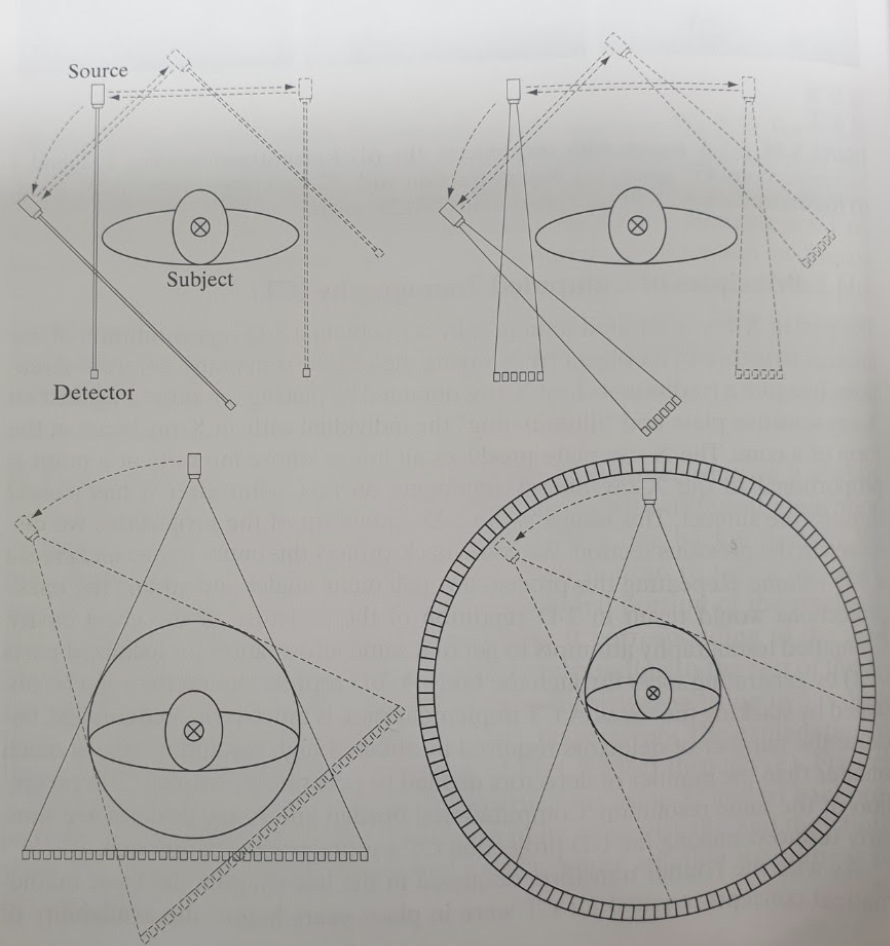
5.11 Image reconstruction from projections




Leave a comment