2.Cartoon filter - Image filtering
Image filtering
1. What is image filtering
- Image filtering
- The task filter the unecessary information and pass the necessary information to image
- Frequency domain filtering
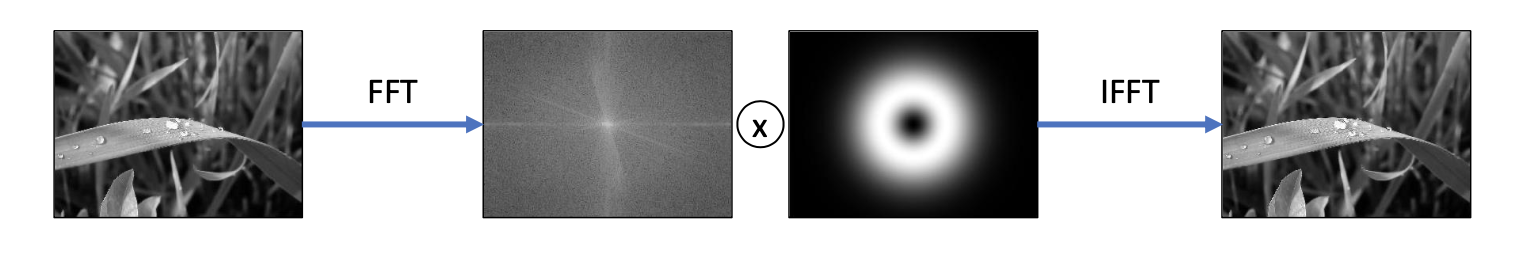
- Spatial domain filtering
- The method directly use the fixel value of video
- Generally Using the mask operation (mask = kernel = window = template)
- The form and value of mask makes the task to define
- Making smoothly image
- Making sharply image
- Edge detection
- Noise reduction
- Example spatial domain filtering
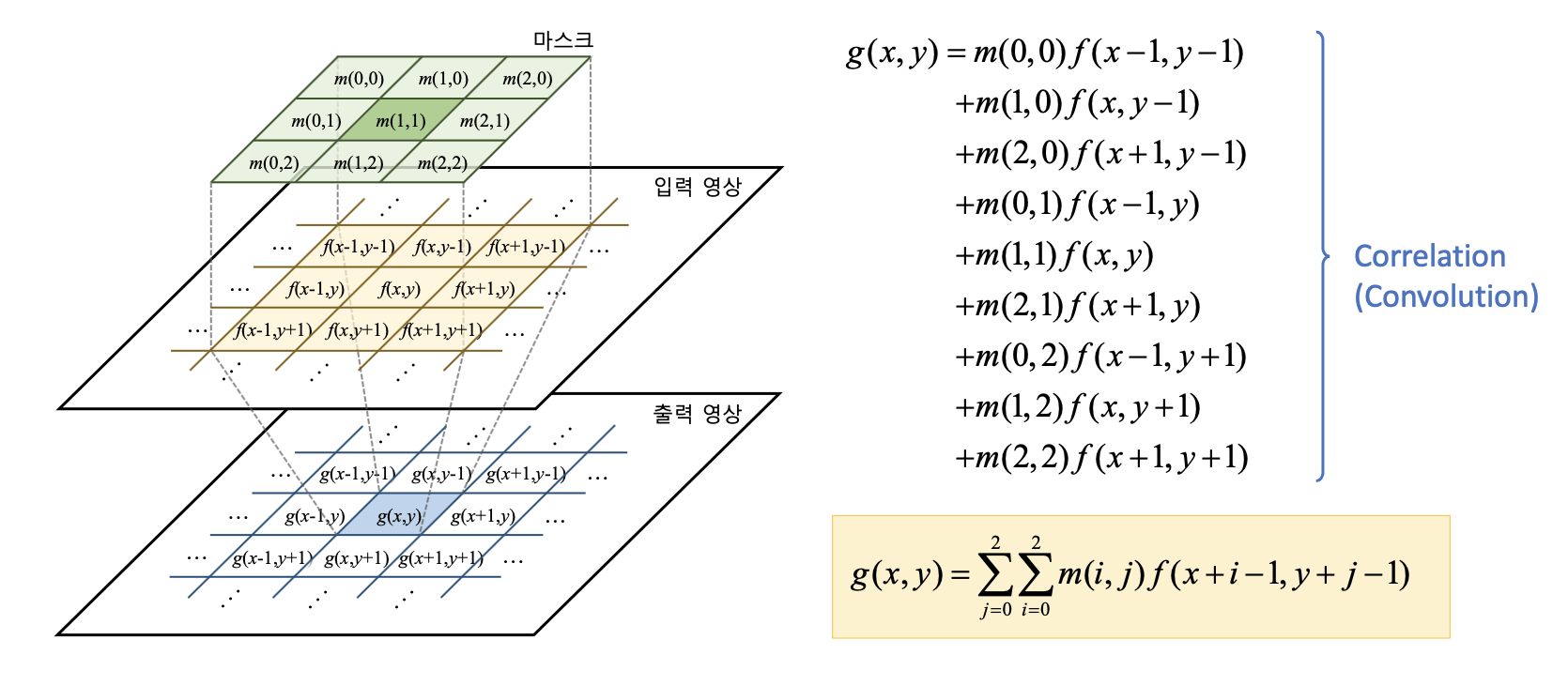
- Basic 2D filtering
cv2.filter2D(src, ddepth, kernel, dst=None, anchor=None, delta=None, borderType=None) -> dst
- src : Input video
- ddepth : Data type of output image ex) cv2.CV_8U, cv2.CV_32F
- kernel : Filter mask metrix
- anchor : Position of fix point
- delta : Additional added value
- borderType : Border pixel Expension method
- dst : Output image
2. Blurring
- Mean filter
- Specific coordination value of image set the arithmetical average of near fixel values.
- The scale value change of each pixel decreases and the sharp edge is going to be smooth. so The effect of noise disappears.
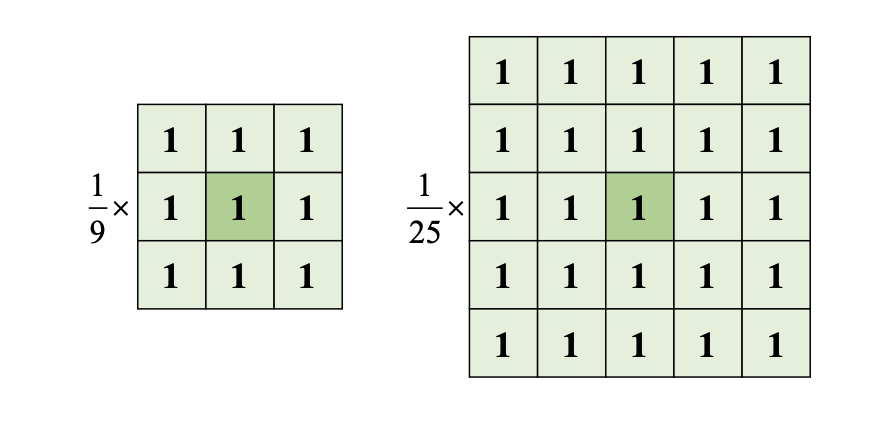
- Mean filtering function
cv2.blur(src, ksize, dst=None, anchor=None, borderType=None) -> dst
- src : Input video
- ksize : Mean filter size ( tuple type - (width, height) )
- dst : Output video
- Mean filter example

3. Gaussian filter
- Disadvantage of the bluring using Mean filter
- From the position of target, Both near pixel and distant pixel use the same weight for calculating the average.
- The distant pixel could be affected
- 1-Dimension Gaussian function
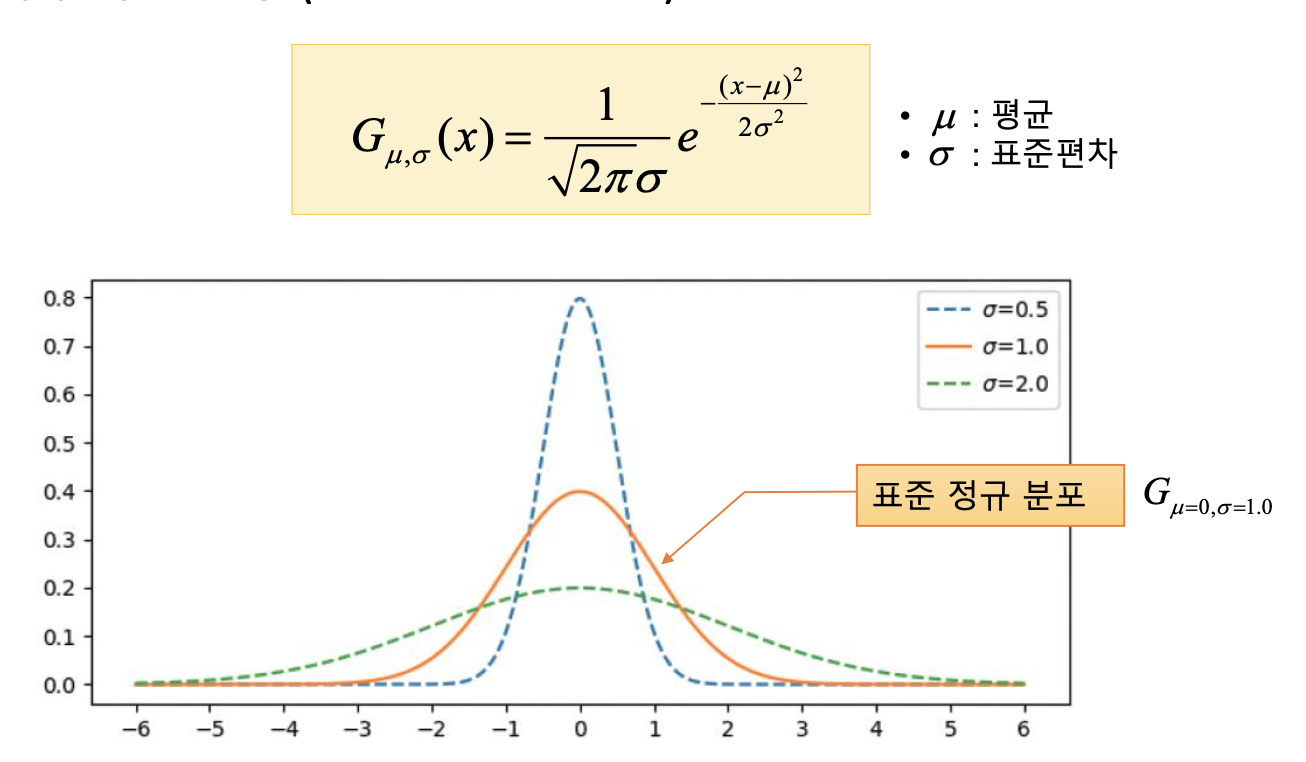
- 2-Dimension Gaussian function
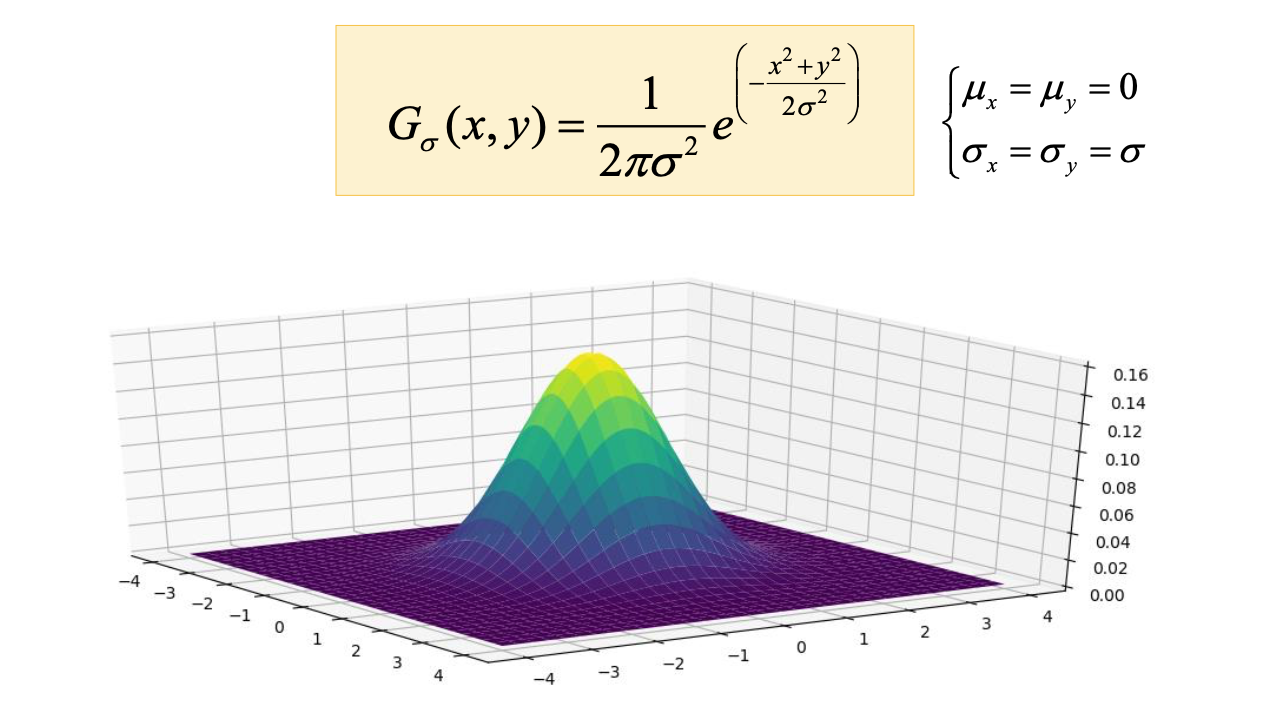
- Gaussian filtering function
cv2.GaussianBlur(src, ksize, sigmaX, dst=None, sigmaY=None, borderType=None) -> dst
- src : Input image
- dst : Output image
- ksize : Gaussian kernel size
- sigmaX : x-directional sigma
- sigmaY : y-directional sigma
- borderType : Edge pixel expension method
- Gaussian filter mask example

4. Sharpening
- Unsharp mask filtering
- Unsharp image, Being the sharped image use to make sharp image.
- Realize unsharp mask filter
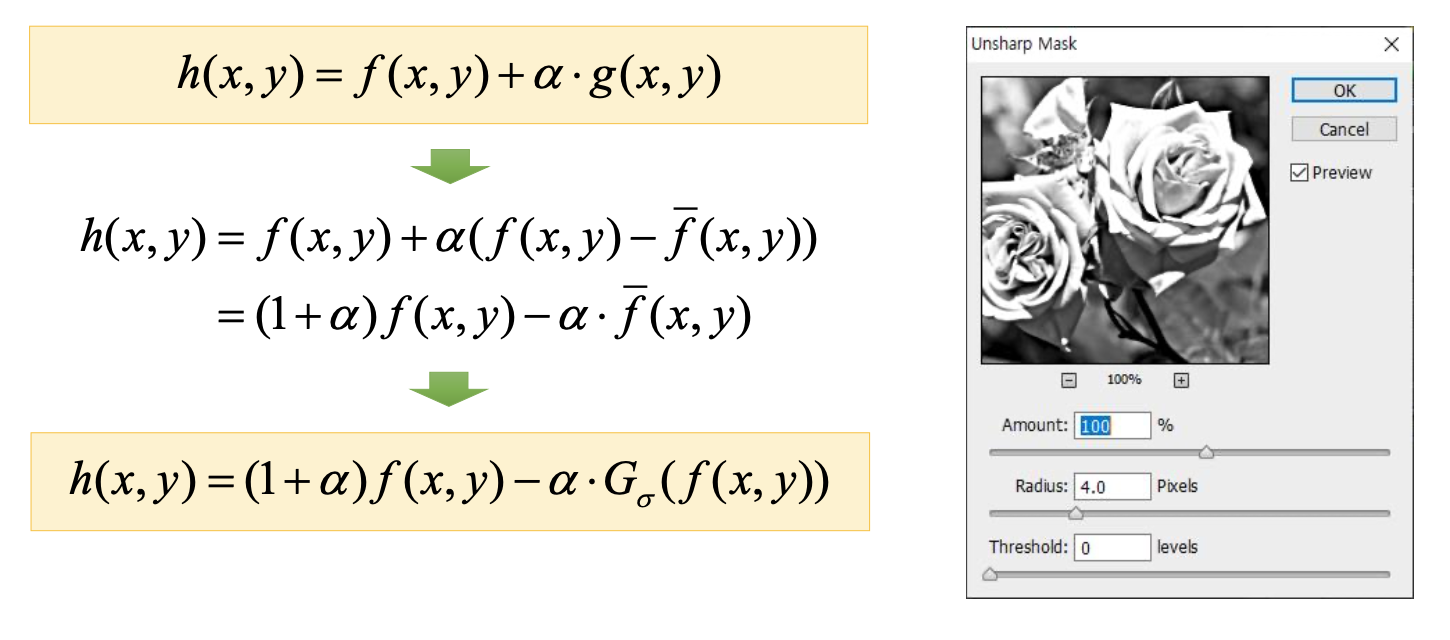
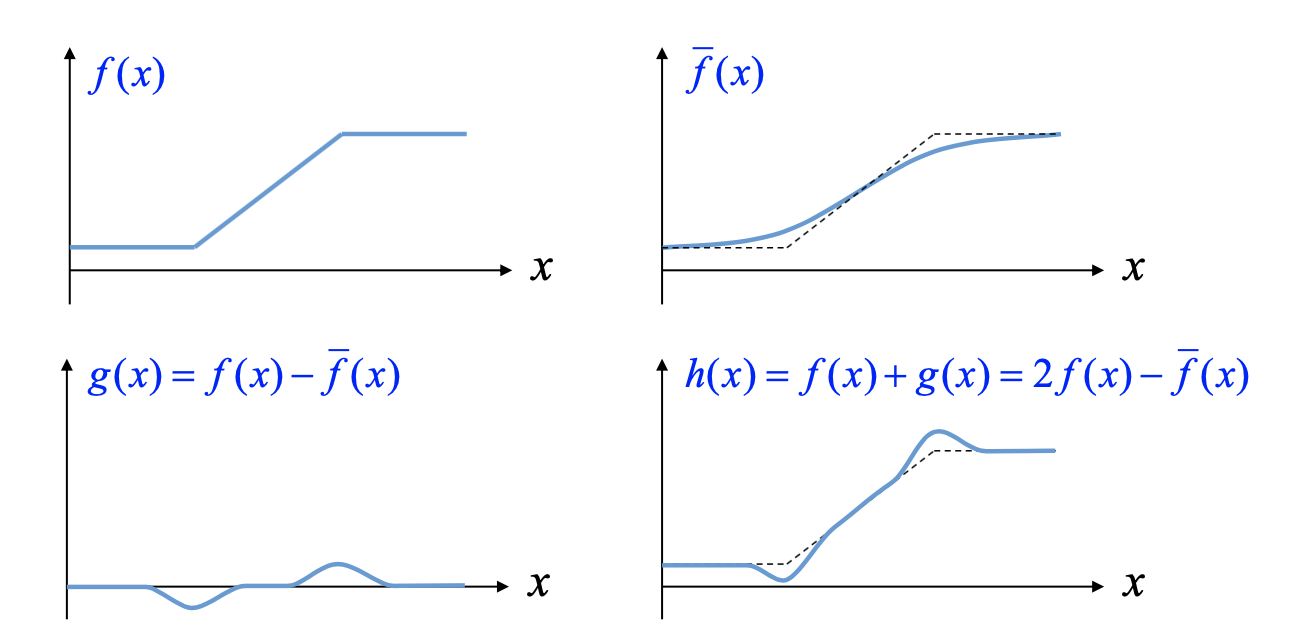
5. Reduction noise - median filter
- Noise of image
- The Unexpected form of the signal be added at pixel value of the image.
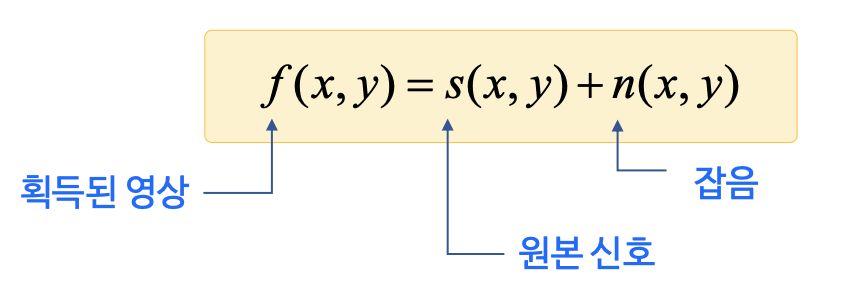
- Sort of noise
- Gaussian noise
- Salt & Pepper

- Median filter
- It replace pixel values by sorting to median value, where are near center position.
- It is effect to reduce the Salt & Pepper noise
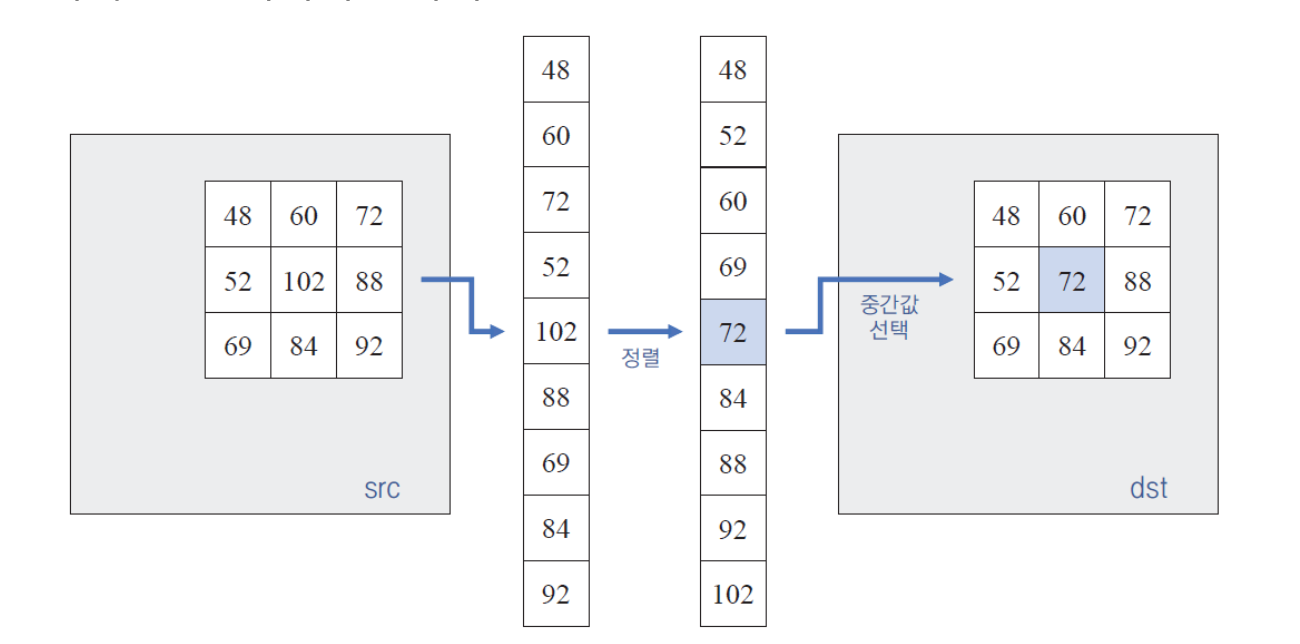
- Median filter function
cv2.medianBlur(src, ksize, dst=None) -> dst
- src : Input image
- ksize : Kernel size
- dst : Output image
- Median filtering example

6. Bilateral filter
- It’s one of edge-preserving noise removal filter
- It have weakness that Median filter and gaussian filter make to average out the pixel value nearby edge.
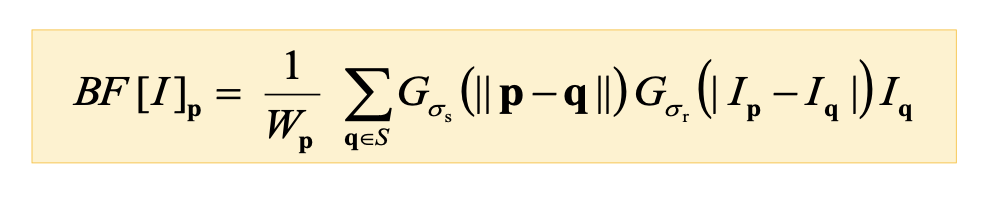
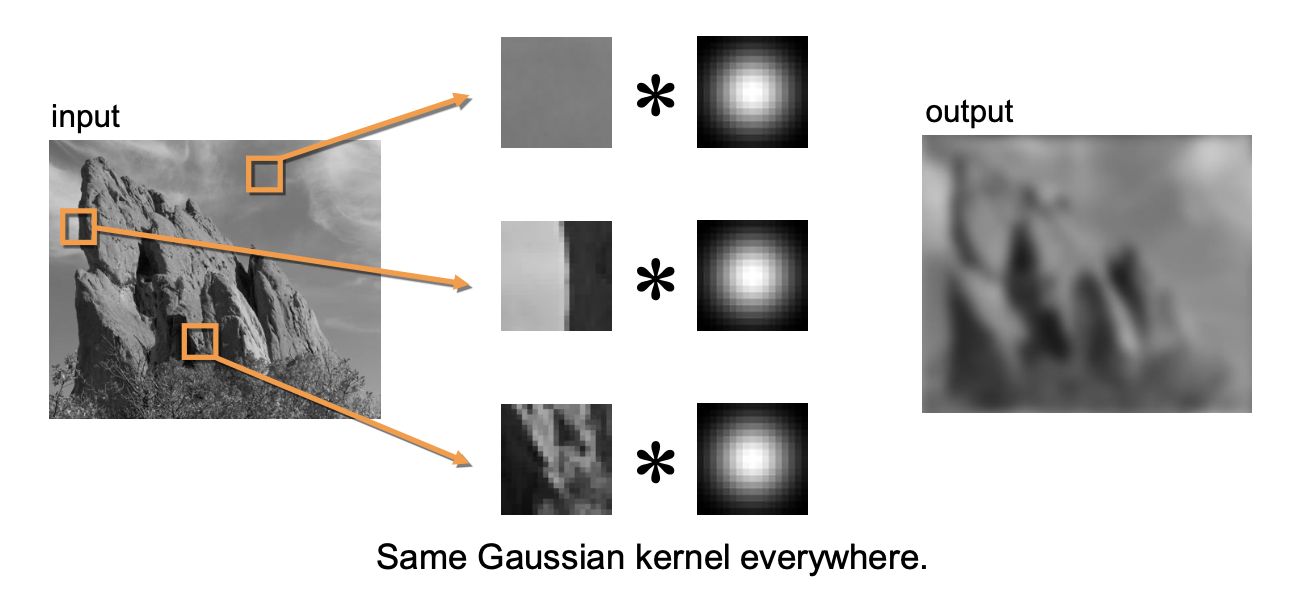
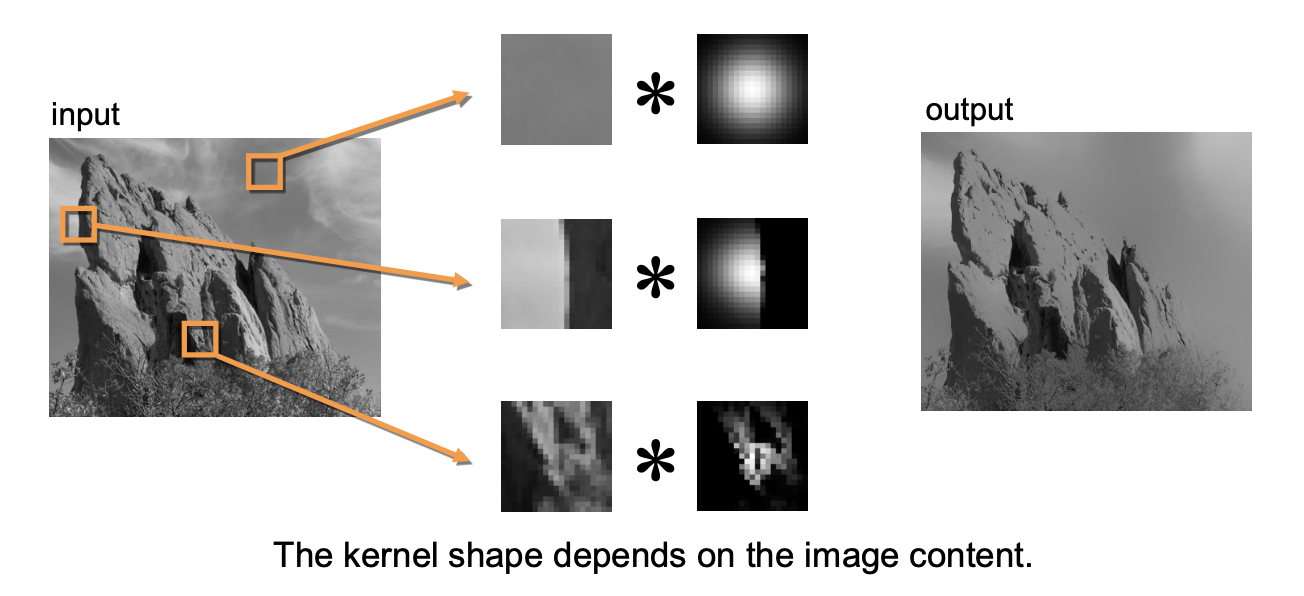
- Normal gaussian filtering : Blurring in the whole image.

- Bilateral filter : Burring in the out of edge
- Bilateral filtering function
cv2.bilateralFilter(src, d, sigmaColor, sigmaSpace, dst=None, borderType=None) -> dst
- src : Input image
- d : Distant(Diameter) of pixel
- sigmaColor : Standard deviation in color space
- sigmaSpace : Standard deviation in coordination space
- dst : Output image
- borderType : Edge pixel processing method




Leave a comment