3.K-means clustering - kNN & K-means algorithm
kNN algorithm
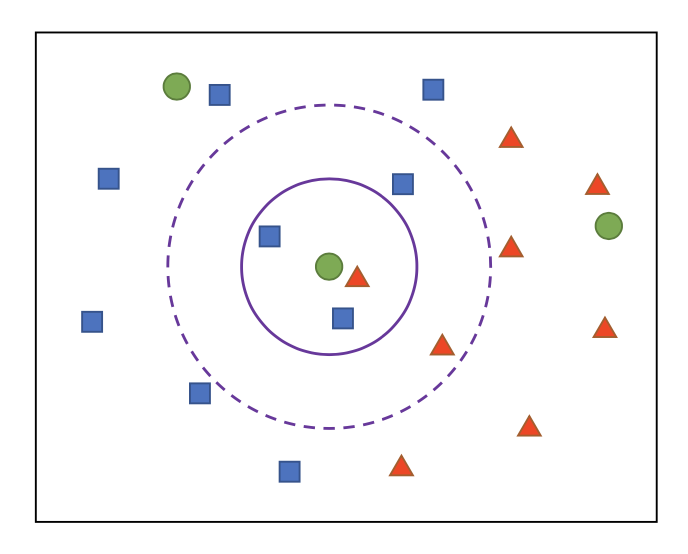
1. What is kNN - Nearest Neighbor algorithm
- It is one of supervise train algorithm for classification or regression that look for train data of K number, where is mostly near by test data in feature space.
- NN vs kNN
- NN : Nearest neighbor (k=1)
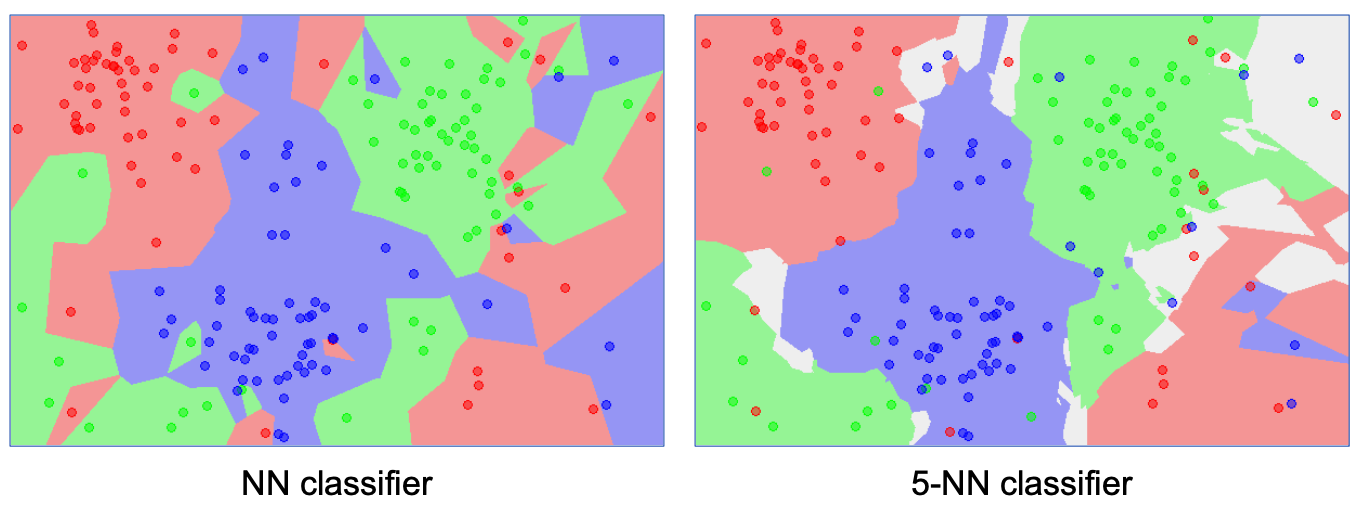
- KNN algorithm object creation
cv2.ml.KNearest_create() -> retval
- retval : cv2.ml_KNearest object
- Input data of classification using the KNN algorithm
cv.ml_KNearest.findNearest(samples, k, results=None, neighborResponses=None, dist=None, flgs=None) -> retval, results, neighborResposnes, dist
- samples : Input sample matric with input vector stored by row unit
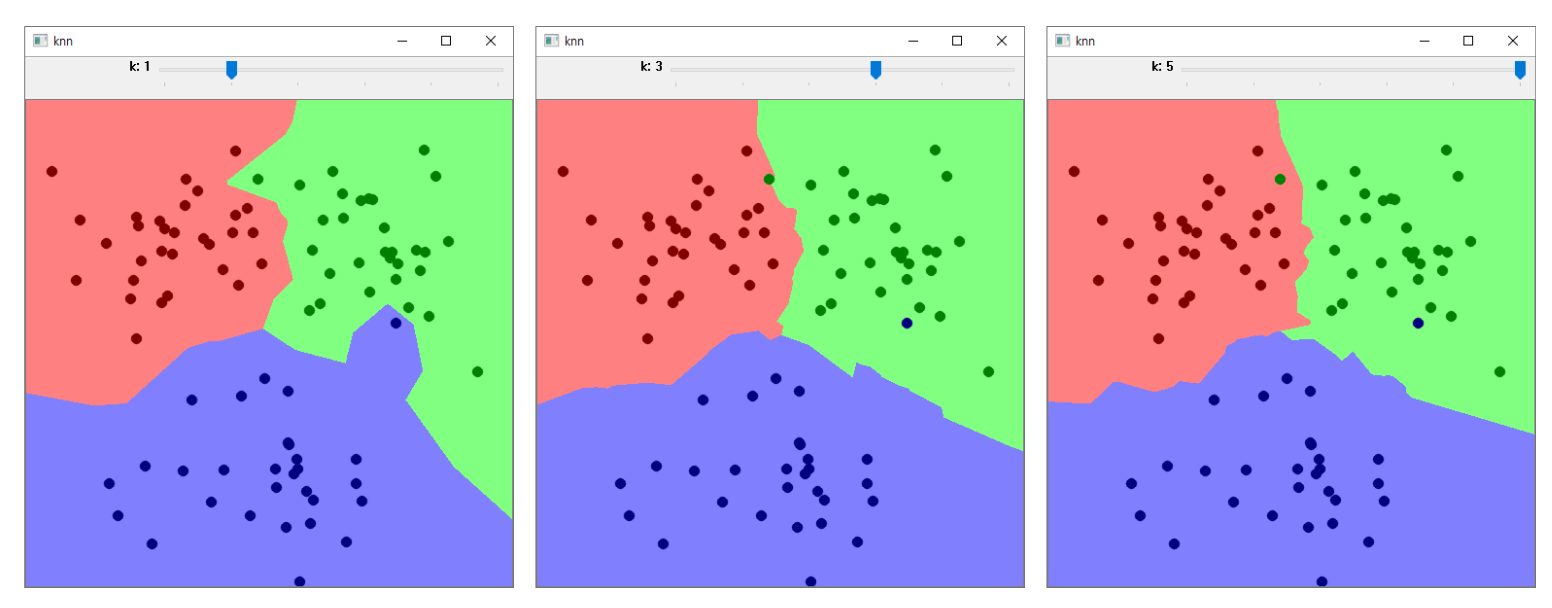
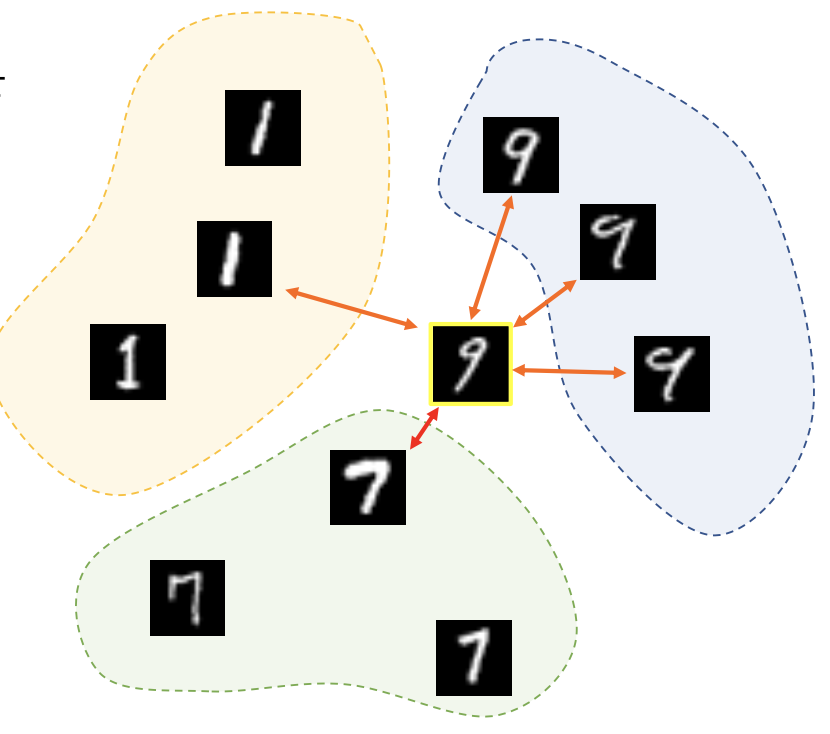
- KNN algorithm poin classification example
2. KNN digit recognition
- If it is the printed digit to setted font, Template matching is possible
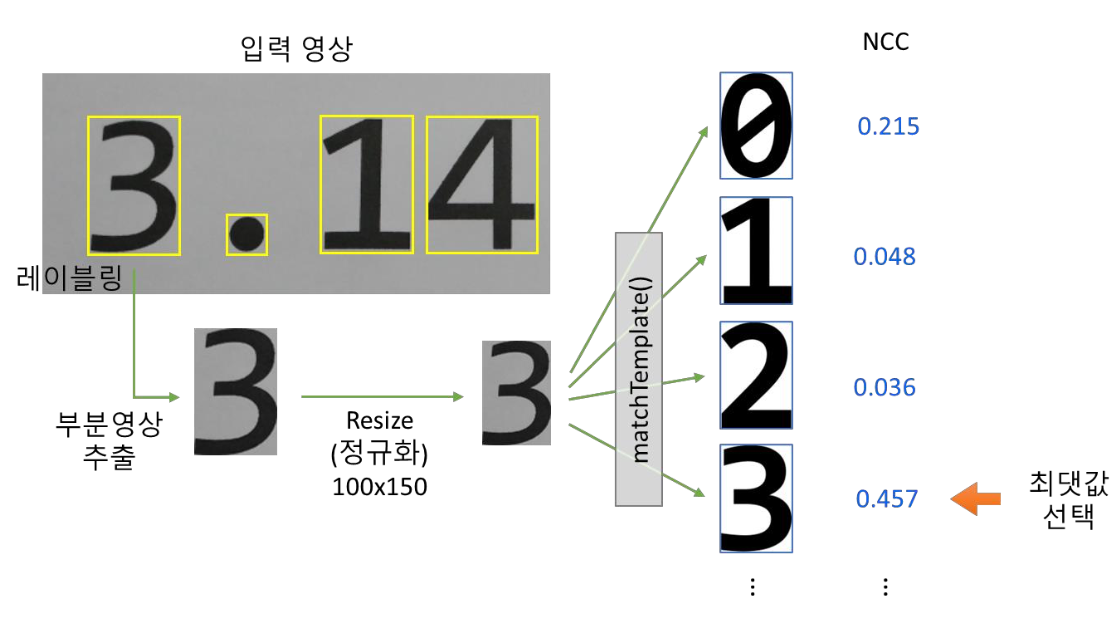
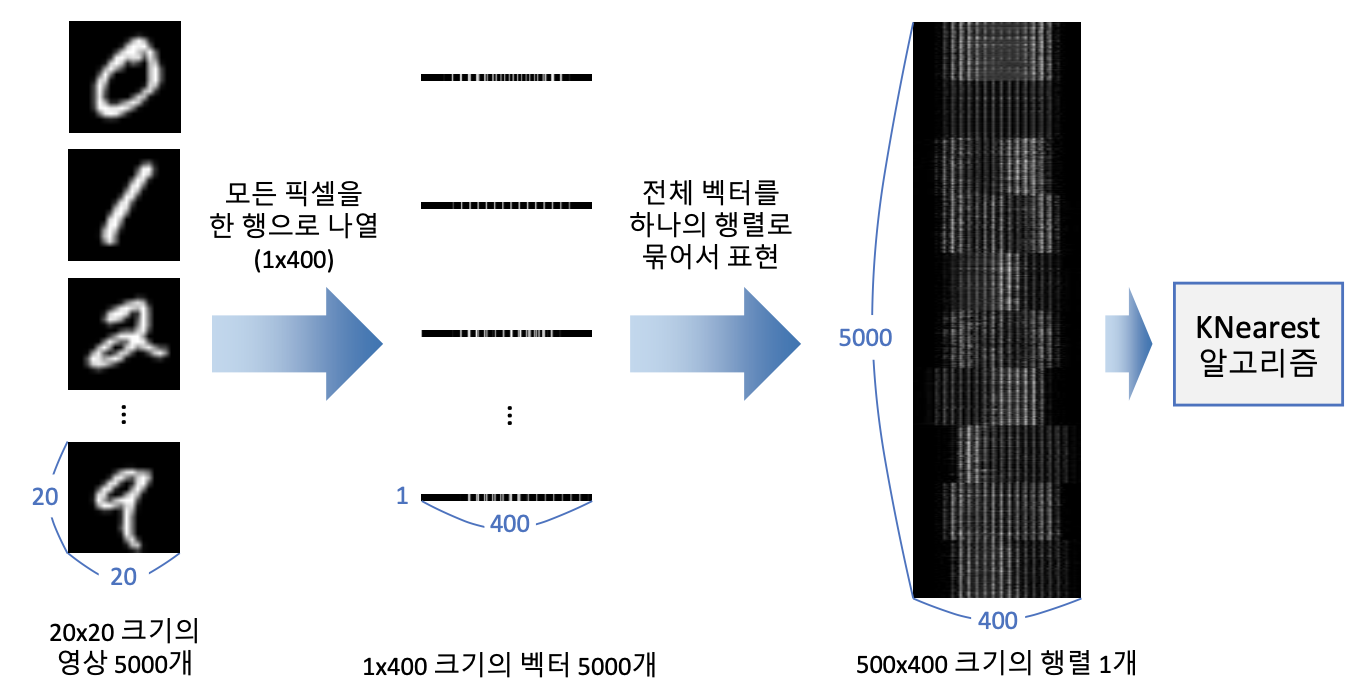
- KNN digit recognition processing
- Making coordination of one point from 400-dimension using pixel value of image 20 x 20
- KNN algorithm point classification in 400-dimension space
- KNN digit recognition flow chart
2. k-means algorithm
- k-means algorithm
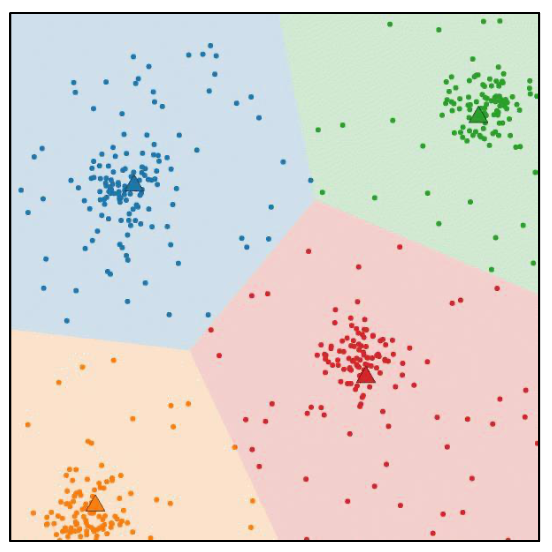
- Cluster algorithm the given data divides section of k number
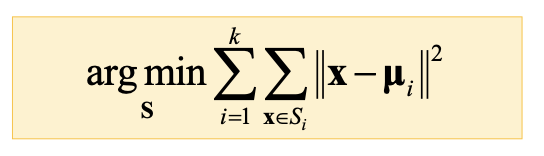
- Cluster algorithm the given data divides section of k number
- Process
- Select random k number center
- Select nearest center to every data
- Recalculate center to each cluster
- Repeat 2~3 process, If center changed
- If not, it’ll end
- Color image segment
- Express each pixel value of input image to the one point of color space
- Perform k-means algorithm in color space
- Translate each pixel value into representive color of k number
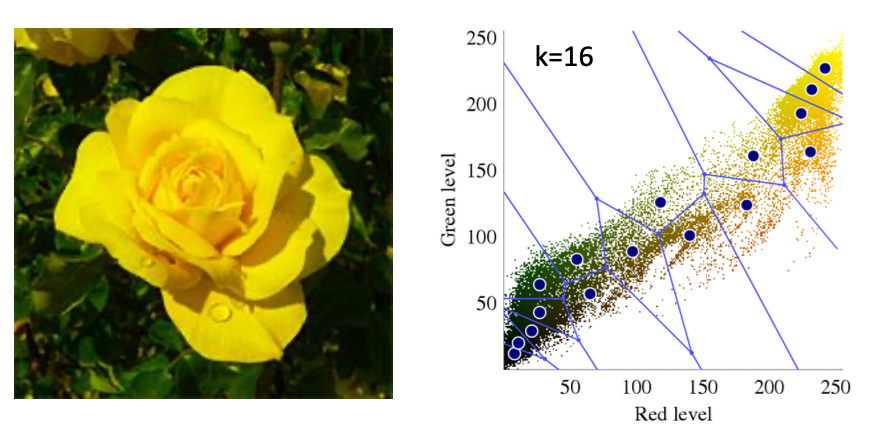
- K-mean cluster code
cv2.kmeans(data, K, bestLabels, criteria, attempts, flags, centers=None) -> retval, bestLabels, centers
- data : train data matrix
- K : cluster number
- bestLabels : cluster set matrix of each sample
- criteria : finish standard
- attempts : repeating number to using another initial label
- flags : initial cent setting method
- centers : matrix for expressing the matrix
- retval : compatness measure
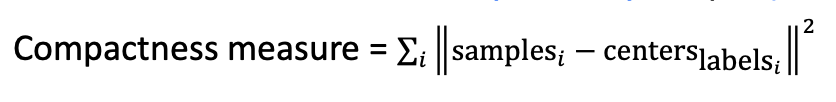
- k-means algorithm example





Leave a comment